Half the World Currently Winning Against COVID
Thursday, 50% of the World Had 10,284 New Cases, 2.6 Cases per Million
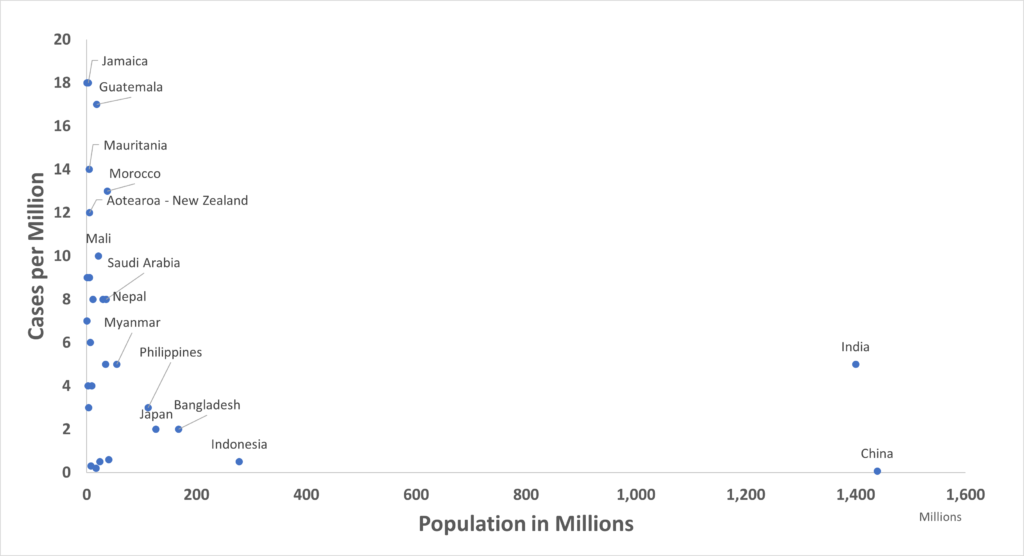
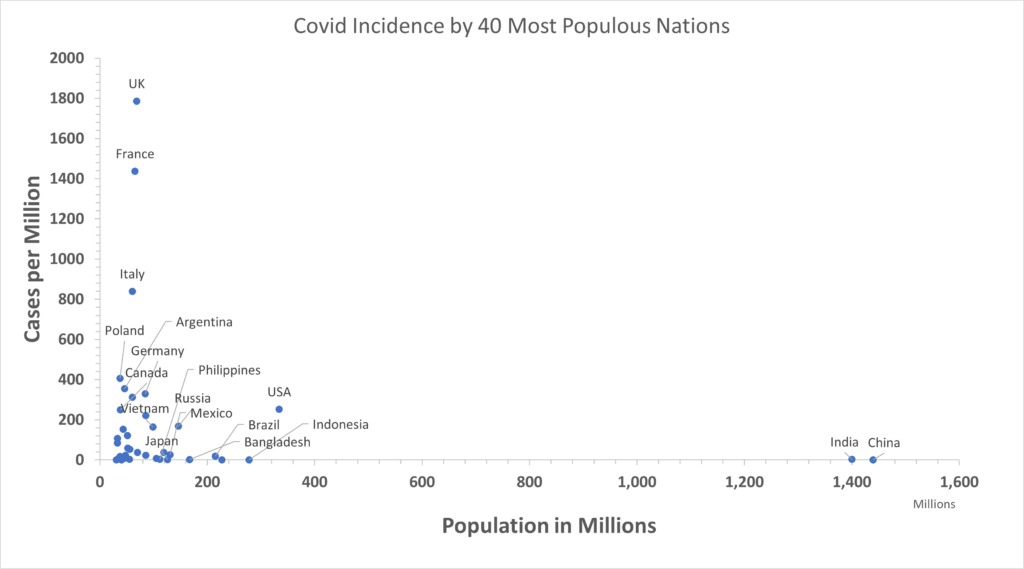
A few countries, including the US and much of Europe, currently have severe Omicron and Delta outbreaks and the majority of COVID-19 cases in the world. Things are not as bad as they appear globally because our focus is skewed, and our vision of the full picture obscured. The figure above shows how 50% of the world’s population reported only 10,284 cases on Thursday. Compare with below, which shows the 40 most populous nations including those with large outbreaks (note change of vertical scale!).
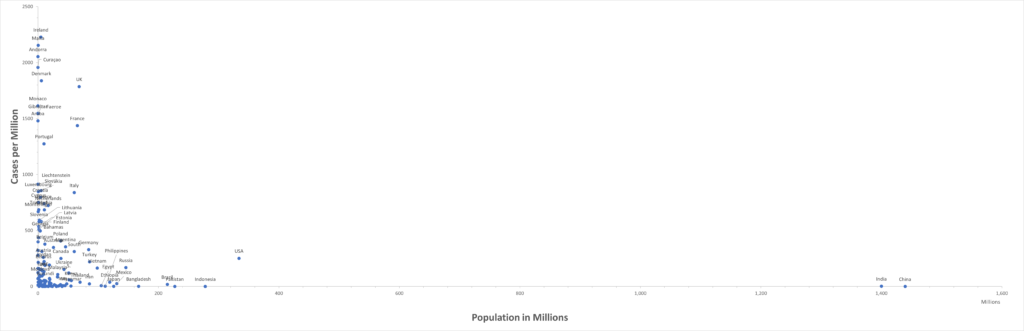
When viewed from a global perspective, most of the world’s population belongs to a country where case numbers are very low, near or below a threshold where elimination is possible. The figure below has all reporting countries. The highest cases per million right now are for Ireland, Malta, Andorra, Curacao, Denmark and the UK. Click on image for full resolution.
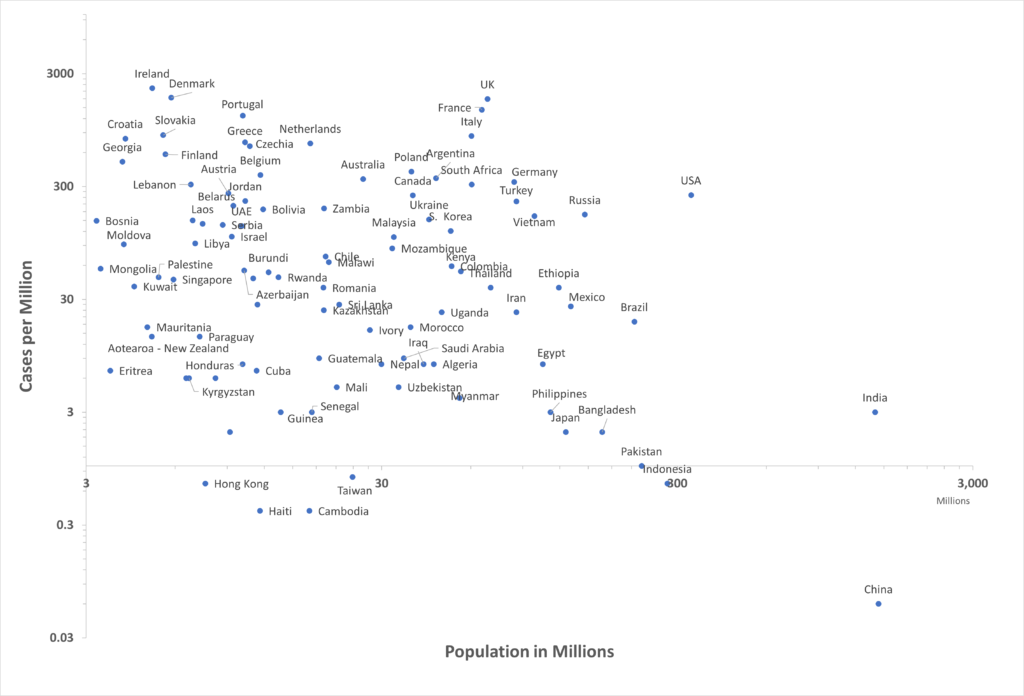
Above is a linear plot followed by a double logarithmic scale plot which shows countries more clearly in relation to each other (equal intervals on each axis are multiplied by the same number). Click on image for full resolution.
Guidance
How to have a safe Christmas: the ultimate checklist (English) – Infographic (WHN)
(Deutsch)
(Français)
(Español)
Resources
Omicron
South Korea reverses plan to “live with COVID-19,” reimposes restrictions across the country to stem spread of the virus.
1,000 critically ill patients a day in South Korea (Korea Herald)
Growing from less than 1% to 13% to 70% in just two weeks, CDC reports more than 70% Omicron prevalence in U.S. (CDC)
“…everyone felt safe because they had all been completely vaccinated and presented negative PCR or rapid antigen tests upon arrival…The Christmas party in Oslo turned into a superspreader event…”
The Omicron Wave Hits Europe (Der Spiegel)
Netherlands locks down, closing all non-essential business following expert advice from the Outbreak Management Team
OMT advises hard lockdown measures (NOS)
Government scientific advisory group advises UK to adopt immediate “very stringent measures” to control Omicron, hospitalizations could peak at 3,000-10,000 per day
Consensus Statement on COVID-19 (SPI-M-O / SAGE)
Federal Scientific Task Force advises Germany take decisive political action to stop Omicron advance, urges clear and concise public communication
Einordnung und Konsequenzen der Omikronwelle (Expertenrates der Bundesregierung zu COVID-19)
Over 80% of the first 785 Omicron variant cases in Denmark were vaccinated or boosted (Eurosurveillance)
Household transmission from Omicron is 2.9X Delta, attack rate in household contacts is 1.5X Delta, and in non-household contacts 3X Delta, risk of reinfection with Omicron is 3X vs. other variants.
17 December UK Health Security Agency Technical Briefing 32 (UK Health Security Agency)
Germany bans travelers from UK and Ireland, citing Omicron concerns (WSJ)
Policy
Waiting one day to adopt NPIs found to increase deaths by 11%; Spanish lockdown twice as effective as Californian Shelter in Place Order
Early adoption of non-pharmaceutical interventions and COVID-19 mortality (Economics & Human Biology)
Waiting one week to adopt NPIs found to triple infections
The impact of policy timing on the spread of COVID-19 (Infectious Disease Modelling)
Among groups living in vulnerable conditions, the pandemic substantially magnified inequality gaps
Aggressive (Level 4) NPIs were associated with slower COVID-19 propagation, particularly in high compliance counties; Pandemic strategies best designed at community-level
Heterogeneity in the Effectiveness of Non-pharmaceutical Interventions During the First SARS-CoV2 Wave in the United States (Front. Public Health)
Data: Tracking non-pharmaceutical interventions in Europe
Covid-19 pandemic policy monitor (Data In Brief)
Economy
Economic health and public health are inseparable, and must be advanced together
From Economic Recovery to Health Resilience (JAMA)
The virus itself is responsible for the majority of the economic damage, rather than control measures
Economic losses caused by increased infections and deaths outweigh economic benefits of lenient infection control
Are less aggressive national lockdowns in COVID-19 associated with enhanced economic activity? (QJM)
Supply-chain dependencies point to need for regional and international policy coordination to reduce economic losses
Mitigation
Mass testing is a powerful tool to rapidly reduce incidence of COVID-19
and Unnecessary obstacles to mass testing (The Lancet)
Pre Omicron recommendations: Policy Recommendations to Identify and Manage Current and Future Variants of Concern
Staying Ahead of the Variants (JHU Center for Health Security)
FDA has identified 3 COVID-19 tests that fail to detect the omicron variant (Med Tech Dive)
In Community,
-The WHN